Before building a redundant architecture, understand each redundancy level’s capabilities and risks. Define N, N+1, and 2N.
What distinguishes 2N from N+1?
N definition: “N” represents the power generator, or battery, you want to copy.
N is the capacity needed to power a facility at full load. The facility was intended primarily for full load with no redundancy. Mission-critical applications would suffer if a component failed or needed maintenance at full load.
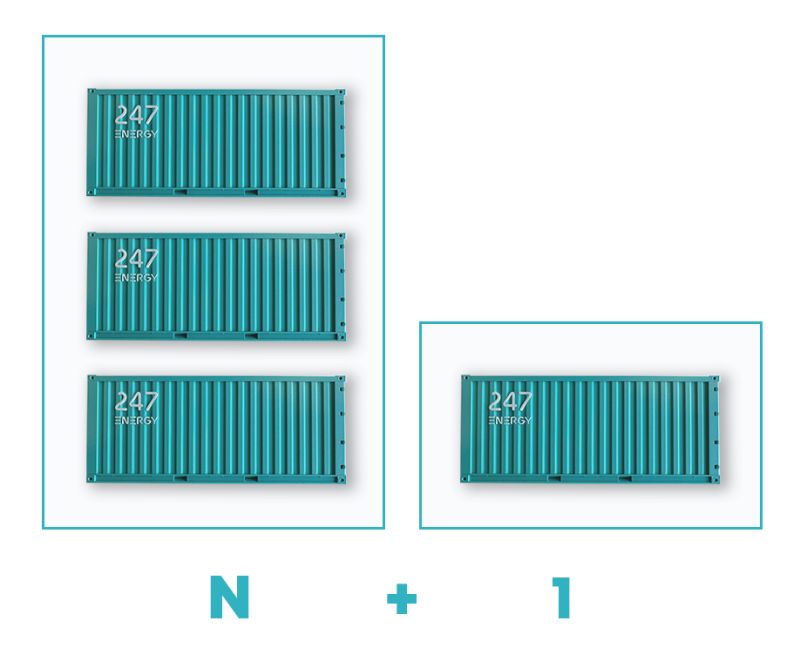
N+1 means
If N is the facility’s capacity, N+1 is an extra component for a single breakdown or maintenance.
2N means
2N is a completely redundant, mirrored system with two distribution systems. They’re unrelated. This means that if one power source fails, the other should still supply power and handle the full load, preventing system downtime.
How do I configure redundancy? Available energy sources, company goals, and budget determine redundancy configuration. N+1 or a combination of sources into a multi-source microgrid? To find the best alternative, get in touch with 247 Energy, your multi-source microgrid partner.